Linux 相關
&, &&, |, ||
| & | command_a & | 在背景執行 command_a |
| && | command_a && command_b | command_a 成功後才執行 command_b |
| | | command_a | command_b | 將 command_a 的 output 作為 command_b 的 input1Ubuntu Manpage: pipe – overview of pipes and FIFOs2Ubuntu Desktop documentation: The Linux command line for beginners3Ubuntu Manpage: pipe, pipe2 – create pipe |
| || | command_a || command_b | command_a 失敗後才執行 command_b |
command_a | grep {regular_expression}
列出 command_a 的 output 中
所有 match {regular_expression} 的 line
Often Used Command
| mv | 把資料夾 {Target} 搬到資料夾 {Destination} 下 |
mv {Target}/ {Destination}/ |
| 把資料夾 {Target}中的內容 搬到資料夾 {Destination} 下 |
mv {Target}/ {Destination} | |
| 重新命名 | mv {OldName}/ {NewName}/ |
Command Line 中括號的意思4Metasyntax
| [] | 可忽略項目 |
| {} | 必須從中選一項,例:{a|b|c} |
| [{a|b|c}] | |
| <> | 必須被替代之項目 |
歷史命令
列出歷史命令 history [列出行數]
不印出行號 history | cut -c 8-
apt(建議使用) vs. apt-get
The apt command line tool provides a higher-level user interface for end users with intuitive commands, resulting behaviors, and security features. In contrast, the command apt-get is a low-level interface that communicates more closely with core Linux processes.
查看被佔用的 port
netstat -tulpnsudo ss -ltnp | grep LISTEN | sed -E 's/.*:([0-9]+).*users:\(\("([^"]+).*/\1 \2/' | sort -n | uniq
type / alias / symbolic link / update-alternatives
範例:[Linux] 更改 Python 版本 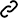
systemd 相關
查看 service 狀態:systemctl status XXX.service
啟用/停用 service:sudo systemctl enable XXX.service
列出所有已啟用 service:systemctl list-units –type=service[ –state=active]
重載 systemd manager 設置:sudo systemctl daemon-reload
查看 service log:journalctl -xeu XXX.service
開機時自動執行腳本 (rc-local.service)
mount / umount
[掛載/卸載] USB 隨身碟
Bash Scripts
註解「# …」
Tip: 修改系統預設文件時,使用「#」以辨認此處非原本預設內容
Hotkeys
移動到 行首/行尾 的快捷鍵 (Ctrl + a/e)
| Ctrl + a | 移動到行首 |
| Ctrl + e | 移動到行尾 |
環境變數
查看環境變數
查看目前所有環境變數
env
查看特定環境變數
echo ${environment_variable_name}
ex: echo $PATH
修改環境變數
永久修改環境變數
修改 profile
路徑:/etc/profile
修改 .bashrc
路徑:/home/{username}/.bashrc
相關實用文章
文字編輯器
Group, Ownership & Permissions
screen
啟用Linux的網路共用資料夾
備份工具 Timeshift
資料夾與檔案的命名
Last Updated on 2026/01/23 by A1go

